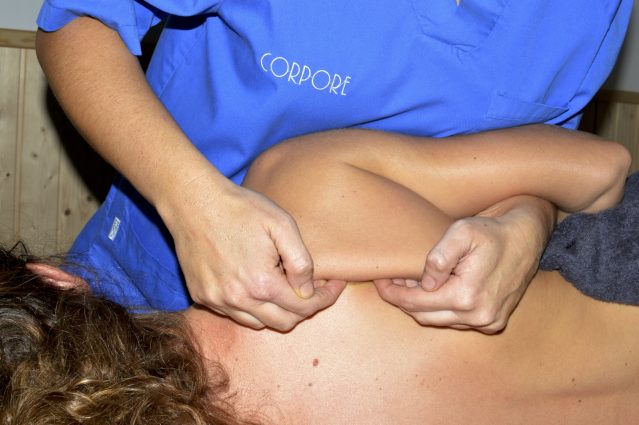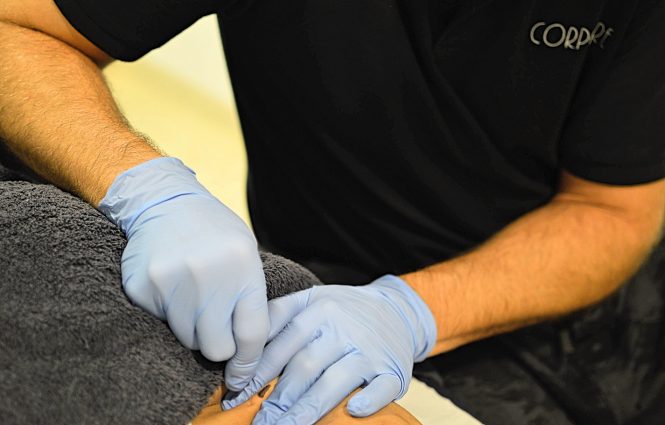
Physiotherapy plays a key role in the prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation of various conditions affecting movement and body function. At our clinic, we offer a comprehensive and personalized approach, combining innovative techniques with the latest scientific evidence to ensure the best results.
To design the most effective treatment, we conduct a thorough assessment to establish an accurate diagnosis. We use advanced tools such as musculoskeletal ultrasound to enhance precision in our interventions. If the condition falls within the scope of physiotherapy, we apply specialized techniques such as dry needling, neuromodulation, manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, and other rehabilitation strategies to relieve pain, improve mobility, and, in many cases, fully restore function.
In cases where our assessment indicates the need for a different medical approach, our multidisciplinary team will refer the patient to the most suitable specialist, ensuring a comprehensive treatment plan and the highest quality of care.
SPECIALTIES
Traumatological Physiotherapy
The treatment protocol focuses on: pain relief, reducing inflammation, restoring mobility, and achieving the patient’s functional recovery.
Rheumatological Physiotherapy
The treatment is tailored to each patient, considering the type and progression of the condition. Key objectives of the intervention include pain relief, prevention of deformities, and restoration of joint mobility.
Respiratory Physiotherapy
Geriatric Physiotherapy
It offers a non-pharmacological treatment alternative, aimed at both the prevention and treatment of various age-related conditions, many of which directly or indirectly affect the musculoskeletal system.
As physiotherapists, our goal is to improve each patient’s well-being while considering their individual capabilities and functionality. We focus on: reducing pain, improving balance, gait retraining for safer and more efficient movement, enhancing joint sensitivity and functionality and maintaining or improving range of motion, strength, elasticity, and flexibility, which are often diminished.
All with the ultimate aim of enhancing our patients’ quality of life.
Cardiovascular Physiotherapy
Treatment of circulatory conditions, primarily affecting the venous, arterial, and lymphatic systems, including edema, lymphedema, varicose veins, heavy legs, phlebitis, and more.
Sports Physiotherapy
Obstetric Physiotherapy
Neurological Physiotherapy
For these patients, our primary goal as physiotherapists is to enhance their ability to perform daily activities.
Pediatric Physiotherapy
Pediatric physiotherapy is equipped to address a wide range of conditions and pathologies affecting babies, children, and adolescents, which may originate from:
•Neurological causes: cerebral palsy, brachial plexus injury (PBO)…
•Genetic conditions: Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis…
•Musculoskeletal issues: scoliosis, clubfoot, flat feet, congenital muscular torticollis…
•Respiratory conditions: bronchiolitis, asthma, seasonal viruses affecting the respiratory tract…
•Systemic diseases: juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
•Children with risk factors: prematurity, benign hypotonia, idiopathic motor delays…
Additionally, pediatric physiotherapy plays a crucial role in prevention, monitoring, and family guidance, offering advice on various concerns such as: baby positioning in different settings, babywearing methods and devices, or digestive discomfort situations.
TECHNIQUES
Tools we use to treat your ailments
Kinesiotherapy
Kinesiotherapy is a set of therapeutic procedures aimed at treating musculoskeletal system pathologies through movement. It can be classified into:
•Passive kinesiotherapy: In this form, the patient does not actively perform the movement; instead, the physiotherapist moves the body segment.
•Active kinesiotherapy: In this form, the patient actively performs the movement.
Objectives:
•Maintain normal functional capacity
•Enhance muscular response
•Recover lost movements
•Treat disabilities such as tetraplegia or paraplegia
•Recover or maintain range of motion
•Prevent joint stiffness
•Prevent and treat respiratory conditions
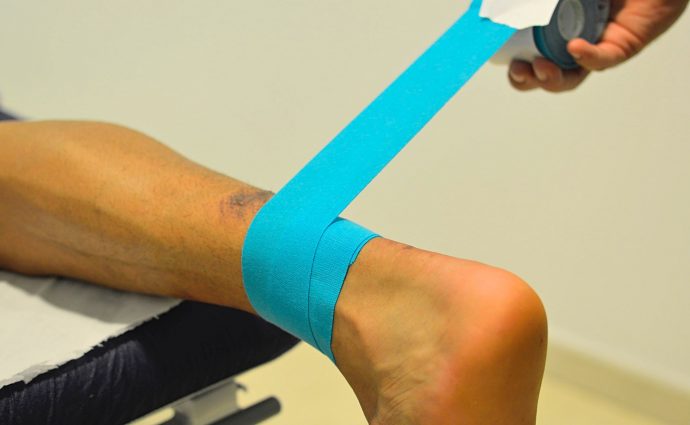
Neuromuscular Taping (Kinesiotaping)
Neuromuscular taping, also known as Kinesiotaping, is a technique that involves the application of an elastic, breathable, and lightweight tape made from braided cotton threads. The tape is coated with an adhesive layer that provides its stickiness. This adhesive is hypoallergenic (latex-free) and mimics the texture of a fingerprint, allowing for improved breathability and skin elevation.
It is used to:
•Relieve pain
•Reduce inflammation
•Minimize bruising
•Provide joint protection
•Improve proprioception
•Correct posture
•And more.
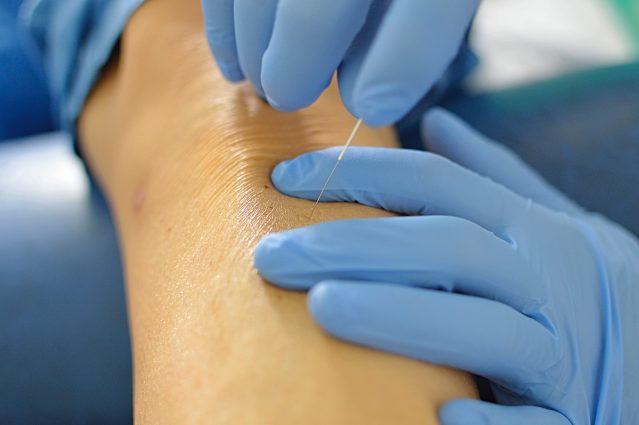
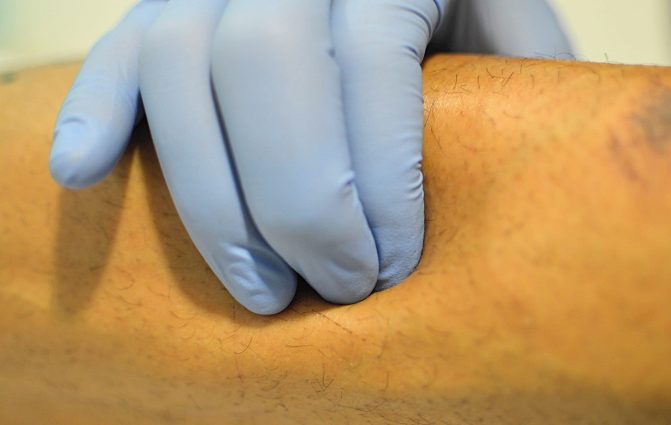
Dry Needling
This technique involves inserting a needle into the body through the skin, without injecting or extracting any substances or fluids. It uses only the mechanical stimulus of the needle and the effects this stimulus has on the body to treat various pathologies, primarily muscular ones (such as tendinopathies, myofascial pain syndrome, etc.).
Dry needling is performed on active myofascial trigger points (MTPs), which are often responsible for referred pain in specific areas of the body, depending on the affected muscle. Myofascial trigger points are areas where muscle tissue is shortened, disrupting the proper flow of nutrients and leading to hypersensitivity in the area when touched.
There are different types of dry needling, including:
•Superficial dry needling
•Deep dry needling, also known as “quick entry and exit Hong method”
•Electroacupuncture (which combines deep dry needling with a TENS current)
Neurodynamics or Neural Mobilization
Neurodynamics, also known as neural mobilization, is a set of techniques focused on the assessment and treatment of painful conditions, dysesthesia, and motor disorders of the peripheral nervous system and meninges. It involves the mechanical stimulation of neural tissue (passive mobilization, sliding, and stretching of the nerves) and the surrounding structures.
The goal is to induce movements in neuromusculoskeletal structures that trigger mechanical and physiological responses in the neural tissue, releasing it from entrapments and dysfunctions. This helps alleviate neuropathic or neurogenic pain, which can also lead to muscle weakness, diminished reflexes, sensory disturbances, and poor capillary circulation.
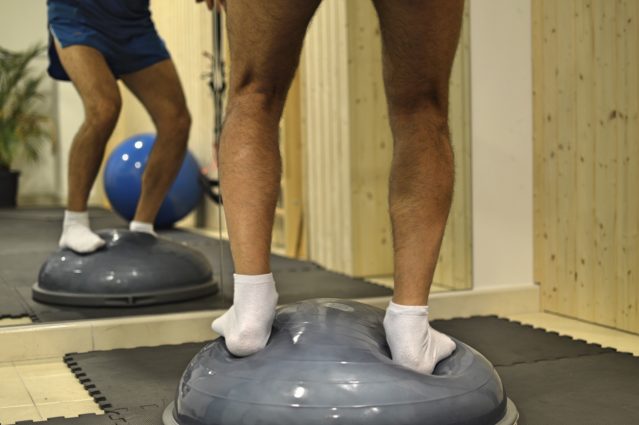
Proprioception Re-education
Proprioception is the sense that informs the body about the position of muscles and the ability to sense the relative position of adjacent body parts. It regulates movement direction and range, allows automatic reactions and responses, and plays a role in the development of the body schema and its relationship with space, supporting planned motor actions. Other functions it influences more autonomously include balance control, coordination between both sides of the body, maintaining the alertness level of the central nervous system, and impacting emotional and behavioral development.
This sense can be impaired after long periods of immobilization, which is why it needs to be re-educated to restore its proper function.
Functional Taping
Is defined as a bandaging technique that limits or inhibits a specific movement that causes pain, while allowing other movements to remain free.
Functional taping is indicated for:
•Grade I and II sprains
•Ligament laxity
•Tendonitis/tendinosis/tendinopathy relief
•Muscle fiber rupture
•Muscle strains and elongations
•Long bone fractures
•Fascia relief
•Intercostal fractures or sprains
•Post-cast removal as a step before rehabilitation
This type of taping is commonly done using tape (an inelastic and rigid band, both longitudinally and transversely) or elastic adhesive bandage (elastic longitudinally and moderately elastic transversely). Before applying the tape, pre-tape is usually used, along with foam protectors on bony prominences.
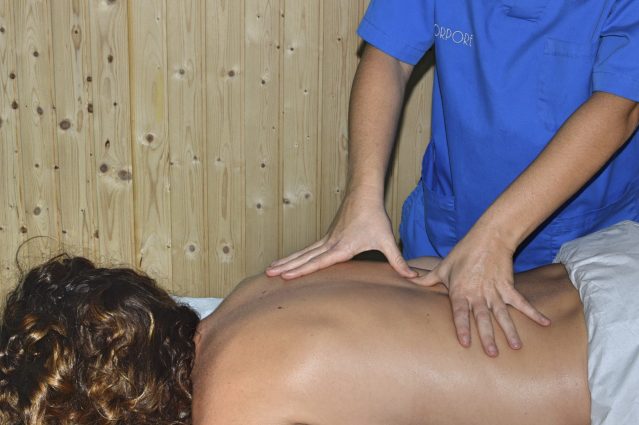
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is a technique defined as the use of various massage techniques for therapeutic purposes. Today, massage is commonly described as “a combination of manual technical movements or maneuvers performed harmoniously and methodically, with hygienic-preventive or therapeutic goals, which, when applied with the hands, allow for the assessment of the condition of the treated tissues.”
It is essential to keep in mind that the physiotherapist’s work is not focused solely on massage therapy. Instead, it is one of the many tools available, forming part of the diverse techniques that can be applied based on each patient’s needs.
Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is a branch of physiotherapy that is defined as the art and science of treating injuries and illnesses through electricity.
Today, technology has developed numerous devices (medical products) for the application of electrotherapy, ensuring no risk of side effects. These include TENS units and high- or low-frequency stimulators.
The main effects of various electrotherapy currents include:
•Anti-inflammatory
•Analgesic
•Improvement of trophism (nutrition and health of tissues)
•Neuromuscular enhancement
•Thermal (in the case of high-frequency electrotherapy)
•Muscle strengthening
•Improved drug delivery
•Reduction of edema
•Pain control
•Improvement in wound healing
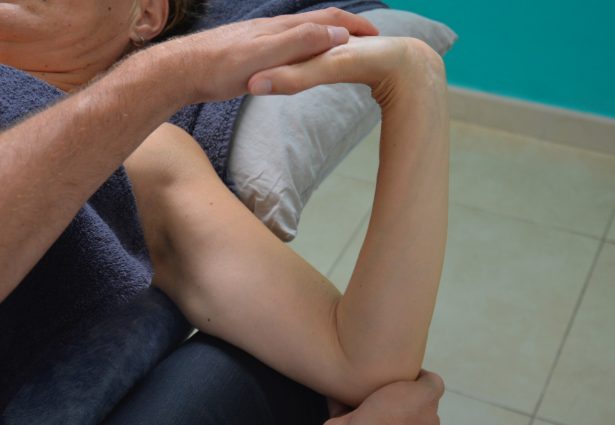
Manual Therapy
Manual therapy is a set of methods and techniques applied manually to the muscles, bones, connective tissues, and nerves for therapeutic and/or preventive purposes. These techniques trigger direct and/or reflex physiological responses that help balance and normalize various muscular, osteoarticular, organic, and functional disorders, as well as their associated painful symptoms.
Therapeutic Exercise
The prescription of exercise by the physiotherapist aims to promote movement of the body or its parts to alleviate, improve, prevent, or slow down the deterioration of health.
The goal is to achieve lasting positive results and provide the patient with tools to manage their own care, making them a much more active and central participant in their health process.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
Manual lymphatic drainage is a specific massage therapy technique aimed at stimulating the reabsorption of fluids through the lymphatic and venous systems, primarily via the superficial system, in order to enhance the elimination of accumulated fluid in the interstitial space or body cavities (edema) and optimize its evacuation.
This technique has draining, neural, and muscle-relaxing effects, as well as benefits for the immune system.
Manual lymphatic drainage is indicated for:
•Lymphatic edema (both primary and secondary)
•Venous edema, specifically in the area of edema
•Traumatic and post-surgical edema, specifically in the area of edema
•Other types of edema, such as those caused during pregnancy or premenstrual syndrome
Fibrólisis instrumental miofascial (FIM)
Es una técnica que surge de la evolución de las técnicas de fricción transversal profunda.
Se define como la realización de una ruptura de fibras (fibrolisis) mediante unos instrumentos (ganchos) con la finalidad de devolver al sistema miofascial su rango de movilidad normal mejorando así el movimiento, el dolor y otros aspectos clínicos relacionados, pero sin traspasar la piel.
Esta técnica es útil en la gran mayoría de patologías del aparato locomotor que cursen con: exudados y hematomas, contracturas musculares, adherencias y acortamientos de tejidos, rupturas de tejidos (fracturas, cirugías…), cicatrices o atrapamientos neurales; entre otros.